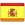
The Factory Audit process
6. Audit Report
Prepare a detailed audit report that includes methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations for corrective actions.
3. Document Review
Review relevant documents and records, such as quality control records, certification documents, employee training records, and compliance reports.
5. Observation and Testing
Observe production processes and conduct tests if necessary to verify that products meet quality standards and specifications.
2. Select an Audit Team
Choose individuals with the necessary expertise in auditing, quality control, and the specific industry.
4. Factory Tour
Conduct a thorough tour of the manufacturing facility to observe operations, worker conditions, and adherence to safety standards.
1. Define Your Objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with the audit, such as assessing quality control systems, compliance with regulations, or evaluating the supply chain.
Process Audits
Process audits are focused on the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing processes. They aim to identify areas for improvement in terms of reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and streamlining production processes for better productivity.
Security Audits
Security audits evaluate the security measures in place at a factory to protect against theft, fraud, and other security risks. These audits are particularly important for factories involved in the production of high-value goods or sensitive materials.
Types of factory audit assessments
Quality Audits
Quality audits focus on the processes and systems in place to ensure that products meet predefined quality standards. These audits evaluate aspects such as material handling, production processes, quality control measures, and final inspection procedures.
Social Compliance Audits
Social compliance audits assess a factory's adherence to social and ethical standards, including labor practices, worker safety, working hours, and discrimination policies. These audits are based on international labor standards and codes of conduct defined by the buying company.
Environmental Audits
Environmental audits examine a factory's environmental management practices, including waste management, resource utilization, emission control, and compliance with environmental regulations. These audits aim to minimize the environmental footprint of manufacturing activities.
Factory Audits for your
Manufacturing facility
What is a factory audit?
A factory audit is a comprehensive assessment conducted to evaluate a manufacturing facility's processes, quality control systems, working conditions, and compliance with legal and industry standards. These audits are typically performed by independent auditors or third-party organizations.
2024. Inspections in Asia. All Rights Reserved.
Why manufacturing audits are important
Factory audits are critical evaluations conducted to assess a manufacturing site's operations, quality management systems, social compliance, and environmental impact. These evaluations are vital for businesses to ensure that their suppliers adhere to agreed-upon standards of quality, safety, and ethical practices. Understanding the importance of factory audits and the different types that might be needed can help companies maintain their reputation, ensure product quality, and support ethical and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Ensuring Quality and Safety
Factory audits are essential for verifying that the products produced meet specific quality and safety standards. This is crucial in industries where safety is paramount, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and automotive. By conducting audits, companies can identify any gaps in the manufacturing process that may lead to quality issues or safety hazards.
Compliance with Laws and Standards
Factories must comply with various local and international regulations and standards. Factory audits help ensure that manufacturing practices are in line with labor laws, environmental regulations, health and safety guidelines, and industry-specific standards. This compliance protects companies from legal liabilities and enhances their market reputation.
Ethical Sourcing and Social Responsibility
Consumers are increasingly concerned about the ethical implications of their purchases. Factory audits that focus on social compliance help ensure that workers' rights are respected, child labor is not used, working conditions are safe, and wages are fair. This not only aligns with ethical sourcing principles but also builds trust with consumers.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental audits assess the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. They help identify ways to reduce waste, decrease greenhouse gas emissions, and manage hazardous materials. Conducting these audits demonstrates a company's commitment to environmental sustainability, which is increasingly important to consumers and regulators.